Resin Plating Process
What is resin plating process?

Resin plating process of Yuken Industry
Resin plating processes can be applied to products in all industries.
This is proven by Yuken Industry’s experience in processing products dating back half a century.
We manufacture products that meet the demands of users in various industries and sectors, such as automotive parts, faucet-related parts, housing facilities, game consoles, electronic parts, etc., under our integrated manufacturing system.
This is the difference! The resin plating process of Yuken Industry
-
Improved corrosion resistance
We deliver interior and exterior parts for domestic car manufacturers, meeting all strict specifications.
-
Quality control system
As the processing division of a chemical manufacturer, our Group possesses state-of-the-art analyzers and testing equipment to guarantee customer satisfaction in the unlikely event of a failure.
-
Improved chrome coverage
Chromium can be applied 10 to 25% better than other resin plating manufacturers.
Processable specifications
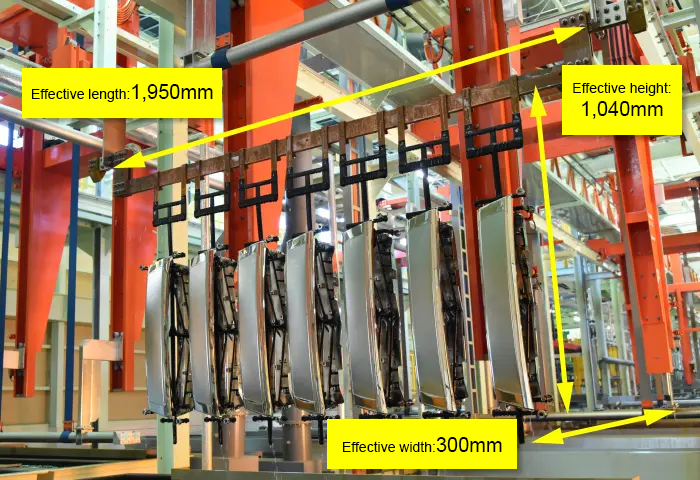
Effective surface of plating process
- Resin materials
- ABS resin, polycarbonate ABS resin
- Processing type
- Copper → Nickel → Chrome
- Resin materials
-
- Copper
- 5~40μm
- Nickel
- 5~40μm
- Chrome
- 0.01~0.8μm
Reasons for plating on resin
Resin plating process (1) Pretreatment process
The process of adding conductivity to a plastic surface that does not conduct electricity.
Soak in an acidic solution
-
Etching
Spoil the foundation
-
Recover
Rinse in water -
Catalyst
Catalyzing
-
Rinse in water
-
Accelerator
Surface preparation
-
Rinse in water
-
Electroless nickel
Conductivity
-
Etching
Provides hydrophilic properties. Dissolves butadiene rubber and creates microporosity on the resin surface.
Resin and metal are physically adhered to each other by the anchoring effect. -
Catalyst
Pd (palladium) catalyst is adsorbed on plastic surfaces.
-
Electroless nickel
Nickel metal is deposited on the plastic surface by a chemical reaction with a Pd catalyst at the core.
Resin plating process (2) Electroplating process
Formation of decorative metal film on plastic surfaces.
-
Nickel strike
Prevention of electroless Ni burning
2~4μm -
Copper plating
Improved leveling
10~20μm -
Soak in an acidic solution
-
Semi-bright Ni plating
Improved corrosion resistance
7~10μm -
Bright Ni plating
Adding metallic luster
3~5μmType 3 nickel plating
-
Joule Ni plating
Prevention of corrosion penetration
3~5μm -
Soak in an acidic solution
-
Chrome plating
Adding metallic luster
0.15μm
-
Copper plating
Strong smoothing action, smoothing out micro-unevenness of the material. It has good spreadability and relieves thermal expansion stress between resin and metal.
-
Type 3 nickel plating
Three types of nickel plating are laminated to retard the progression of corrosion.
-
Chrome plating
It has excellent corrosion resistance, high film hardness, and excellent abrasion resistance. It has a beautiful bluish color.
Material considerations for resin plating
Points to be noted for product configuration
Corners (sharp edges) should be rounded to 0.2R or more.
It is harder than resin. However, it is also more brittle. Therefore, it is necessary to be innovative in design.
- Convex corners cause current to concentrate, resulting in poor appearance (scorching).
- Concave corners are difficult to plate.
- Easy to crack due to stress concentration during thermal buffering.





