PVD Treatment
What is PVD treatment?
PVD treatment is a surface modification technology that produces a thin film of ceramics on a metallic material.
With this thin film, metal materials can obtain various functions such as improved slipping and resistance to abrasion, galling, welding, heat, and corrosion.
Its wide range of applications include cutting tools, molds, automotive parts, watches, medical equipment, and others.
Comparison of various surface modification technologies
| Treatment method | PVD *1 | CVD *2 | TD *3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Plasma reaction | Thermochemical reaction | Thermo-reactive deposition and diffusion |
| Membrane type | TiN、TiCN、TiAlN、CrN、DLC etc | TiN、TiC、TiCN、Al2O3 etc | VC |
| Treatment temperature (℃) | 200~600 | 700~1200 | 1000~1100 |
| Dimensional accuracy |  |
 |
 |
| Adhesion |  |
 |
 |
| Re-treatment |  |
 |
 |
*1 Physical Vapor Deposition
*2 Chemical Vapor Deposition
*3 Toyota Diffusion Coating Process
Advantages of PVD treatment
In recent years, molds have tended to become more precise, and the PVD method, with its low distortion, is suitable for meeting this demand, and it has the following major advantages over the CVD and TD methods.
(1) Low treatment temperature minimizes dimensional changes of treated materials
(2) Further functional improvement is possible by combined treatment with nitriding, a hardening treatment.
(3) Multiple reuse is possible by reprocessing the molds
PVD film formation process
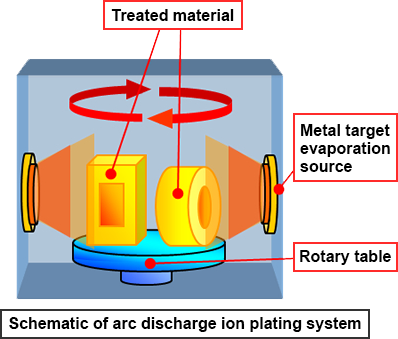
Ion plating methods include arc discharge, electron beam, and holocathode, but among them, the arc discharge method, which is considered to be the most typical, is introduced here.
Arc discharge ion plating system
With the arc discharge type equipment, the workpiece is placed on a rotating table, and while the table is rotating, a metal target inside the equipment is evaporated and deposited on the surface of the workpiece together with reaction gas to form a film. (Right figure)
Film formation process
The following is a model diagram of the film formation process. (Example: TiCN coating)
Vacuuming → Heating → Applying negative voltage
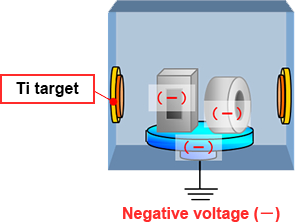
- 1.
- After creating a vacuum in the equipment, heat the treated material.
- 2.
- Apply a – (negative) voltage to the treated material.
Introduction of reaction gas, evaporation of metal target
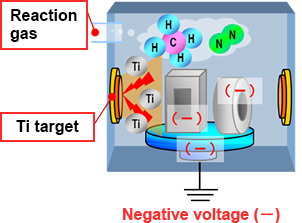
- 3.
- Introduce nitrogen or hydrocarbon gas as a reaction gas.
- 4.
- The metal target (Ti) in the equipment is evaporated by arc discharge, which generates metal ions.
Film formation
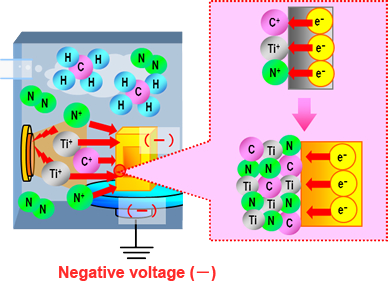
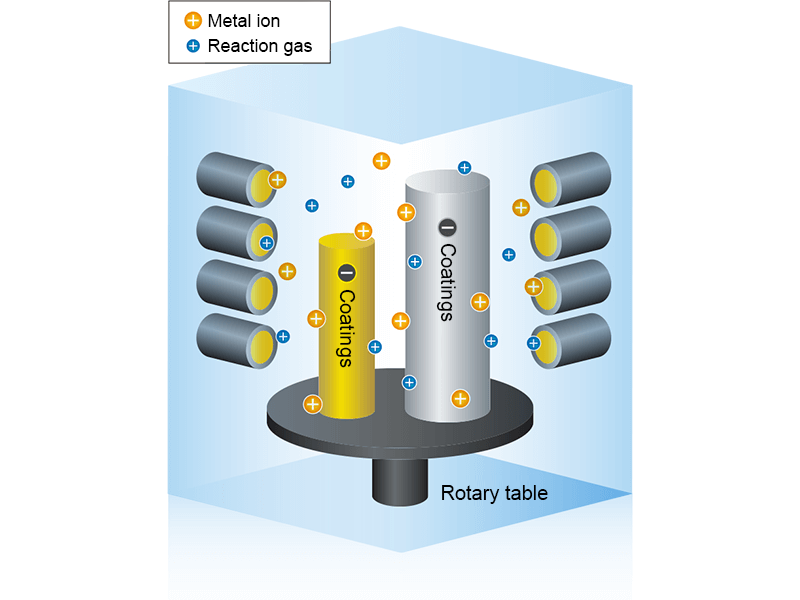
- 5.
- The + (positive) charged metal and gas are attracted to the – (negative) charged treatment material and receive electrons (e-) from the treatment material, thus forming a film.
